Introduction to Hadoop

What is Hadoop?
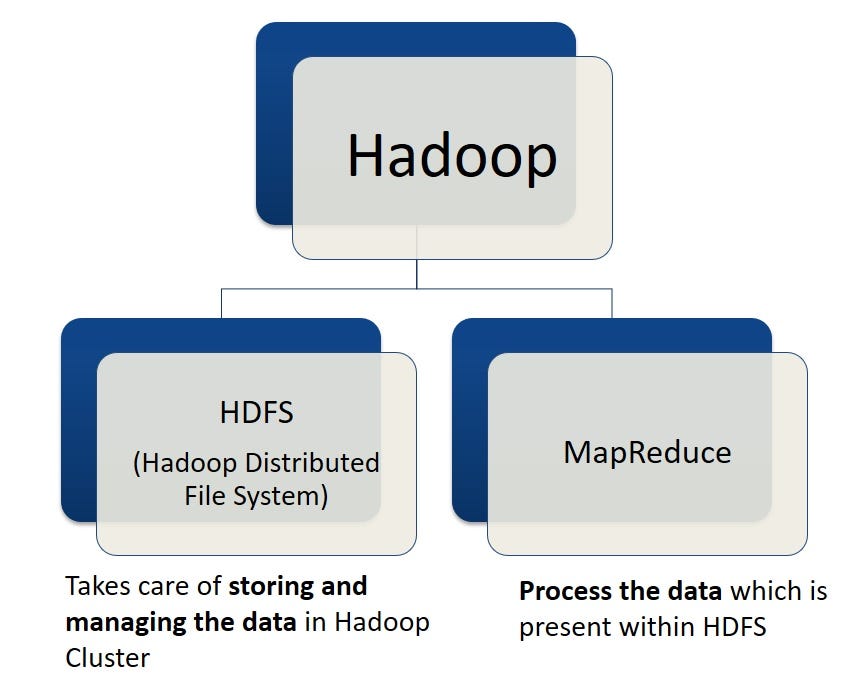
Hadoop is a framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. It uses the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for storage and MapReduce for processing. It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage. Hadoop’s core functionality focuses on big data management, but it can indirectly support ML by providing the infrastructure for storing and processing the data used for training ML models. Apache Spark, which runs on top of Hadoop, is commonly used for distributed ML model training due to its in-memory processing and ML libraries (MLlib). The key components of Hadoop include:
-
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): This is the storage system of Hadoop, which stores data across multiple machines without prior organization. Here’s how it works:
NameNode: This is the master node that manages the metadata of the files stored in the cluster (e.g., file names, permissions, and the locations of the data blocks). It doesn’t store the actual data. DataNode: These are the worker nodes that store the actual data. Each file is split into blocks, and these blocks are distributed across various DataNodes.
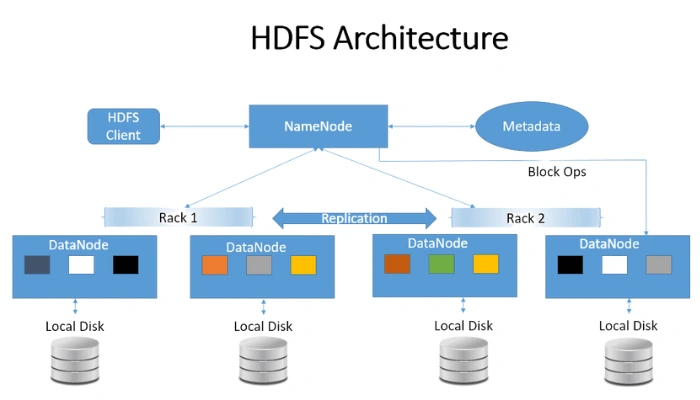
How HDFS works: - When you want to store a file, it gets divided into smaller blocks (typically 128 MB or 256 MB). - These blocks are then stored across different DataNodes. - Each block is replicated multiple times (usually three) to ensure fault tolerance. If one node fails, the data can still be retrieved from another node.
-
MapReduce: This is the processing technique for analyzing data in a distributed fashion. It breaks down tasks into smaller parts, processes them in parallel, and then combines the results. It works in two main phases:
Map Phase: Takes input data and converts it into a set of key/value pairs. Each key/value pair is processed independently by different mappers.
Reduce Phase: Takes the output from the map phase and combines the intermediate data into smaller sets of key/value pairs. This phase typically performs some kind of aggregation or summarization.
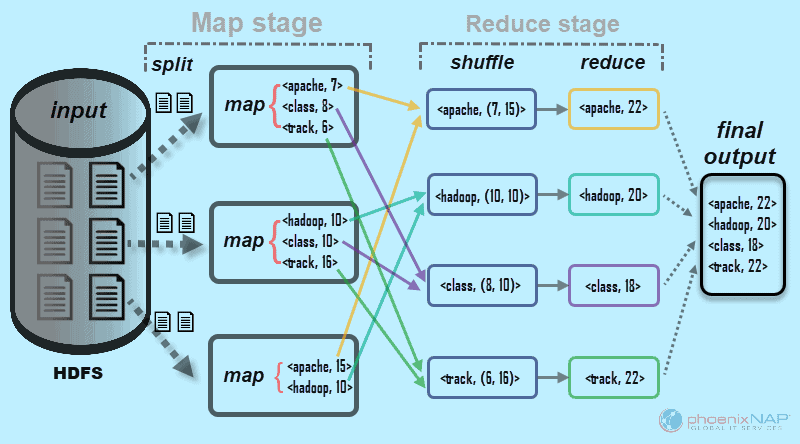
How MapReduce works:
- The input data is split into chunks that are processed by map tasks in parallel.
- Each map task processes its chunk and produces intermediate key/value pairs.
- The intermediate data is shuffled and sorted, then sent to reduce tasks.
- Each reduce task processes its set of intermediate data and produces the final output.
-
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator): YARN is the resource management layer of Hadoop. It manages and schedules resources across the cluster and ensures that tasks are allocated appropriate resources.
ResourceManager: It is the central authority that manages resources and schedules applications running on the cluster. NodeManager: Runs on each node and is responsible for managing the node’s resources and monitoring the node’s health. ApplicationMaster: Manages the lifecycle of applications, handling the execution of individual tasks within the application.
How YARN works:
- The ResourceManager receives requests for resources from applications.
- It decides which applications get the resources based on policies.
- The NodeManager on each node reports resource availability and health status to the ResourceManager.
-
The ApplicationMaster negotiates resources with the ResourceManager and works with NodeManagers to execute and monitor tasks.
- Hadoop Common: Hadoop Common contains libraries and utilities needed by other Hadoop modules. It provides the necessary Java files and scripts to start Hadoop.
Putting It All Together
Here’s how these components work together to enable distributed processing:
- Storage: HDFS stores large data sets across multiple machines, ensuring fault tolerance and high availability.
- Processing: MapReduce processes these large data sets in parallel, breaking tasks into smaller units that can run simultaneously.
- Resource Management: YARN manages resources and schedules tasks, ensuring efficient utilization of the cluster.
- Common Utilities: Hadoop Common provides the necessary tools and utilities to support these processes.
Example Scenario
Imagine you have a huge log file that you want to analyze. Here’s how Hadoop would handle it:
- Store the log file: HDFS splits the file into blocks and distributes these blocks across multiple DataNodes.
- Map Phase: The MapReduce job is submitted, and the map phase processes the log file blocks in parallel on different nodes.
- Shuffle and Sort: Intermediate results from the map phase are shuffled and sorted.
- Reduce Phase: The sorted data is processed by reduce tasks, which aggregate and summarize the results.
- Final Output: The output is written back to HDFS, where it can be accessed for further analysis.
Role of Hive in Hadoop
Hive is a data warehousing tool built on top of Hadoop. It was developed by Facebook and later open-sourced. Hive allows users to query and manage large datasets residing in distributed storage using SQL-like syntax. Here’s how Hive makes life easier for those dealing with big data:
- SQL-like Queries: HiveQL, the query language for Hive, is similar to SQL, which makes it easier for those familiar with relational databases to run queries on big data.
- Abstraction over MapReduce: While Hadoop’s MapReduce requires programming in Java or other languages, Hive abstracts this complexity by allowing users to enter queries in HiveQL, which it then converts into MapReduce jobs under the hood.
- Integration with Hadoop Ecosystem: Hive works well with HDFS and other components of the Hadoop ecosystem, making it versatile and powerful for data warehousing tasks.
What you should know before starting to learn Hadoop?
1. Basic Programming Knowledge
- Java: Hadoop is primarily written in Java, so understanding Java is crucial because many Hadoop components and APIs require Java programming skills.
- Python/Scala: These languages are also popular in the Hadoop ecosystem, especially for writing scripts or using Apache Spark, which can run on Hadoop.
2. Fundamentals of Linux
- Linux Operating System: Hadoop runs on Linux, so basic skills like handling files and directories, navigating the command line, and running shell scripts will be very helpful.
3. Understanding Databases and SQL
- SQL: Since Hadoop interacts frequently with database systems and uses Hive (which employs SQL-like querying), knowledge of SQL is essential.
- Database Principles: Basic knowledge of how databases work, including data storage, retrieval, and management.
4. Basic Networking Concepts
- Network Basics: Understanding how computers communicate over networks, basics of IP addresses, and ports can be very helpful, especially when configuring and managing Hadoop clusters.
5. Distributed Systems
- Concepts of Distributed Computing: Understanding the basics of distributed systems such as data distribution, parallel processing, and fault tolerance. This will help you grasp how Hadoop processes large data sets across multiple machines.
6. Data Structures and Algorithms
- Efficiency in Data Handling: Knowledge of data structures (like trees, graphs, arrays, etc.) and algorithms helps in optimizing data processing tasks and understanding how Hadoop manages data.
7. Introduction to Big Data
- Big Data Concepts: Understand what constitutes big data, challenges associated with big data processing, and the role of technologies like Hadoop in solving those challenges.
8. Learn Apache Hadoop
- Core Hadoop Components: Learn about HDFS for storage, MapReduce for processing, and YARN for cluster management.
- Hadoop Ecosystem: Familiarize yourself with tools that are commonly used with Hadoop, such as Apache Hive, Apache Pig, and Apache Spark.
- Hands-On Practice: Setting up a small Hadoop cluster using tools like Hadoop MiniCluster or using cloud services to practice running Hadoop jobs.